Bela P. Bozsik, M.D.
Medical
Secretary of the Hungarian Lyme Borreliosis Foundation
(LBF website at http://Lymenet.hu);
BP retired as working physician in 1999, but he continues his research
in Lyme
borreliosis and related infections in private clinic.
Email:
bpbozsik at freestart.hu.
Office & Postal
address: Dr. Bela
Bozsik, Lyme Borreliosis Foundation, Tetenyi St. 98, building B
Budapest, XI Hungary H-1119
Curriculum
Vitae:
Born in Budapest, Hungary, Sept. 9, 1942, as son
of Pal Bozsik and Maria Klinga; married to Marta Schleer, Dec. 4, 1968;
children: Bela, Andras Pal, Attila Peter.
Memberships:
Member of N.Y. Acad. Sci.
Member of Society for Christian
Physicians, Roman Catholic.
1960-61: Worker Lenin Metall. Works, Miskolc, Hungary.
1966: Graduated
as MD from Semmelweis Med. U., Budapest.
1966-74: Pathologist
St. Istvan Mcpl. Hosp., Budapest.
1974-99: Researcher.
Nat. Inst. Hygiene, Budapest. A
new method for evaluating the immunohemolytic activity of Complement
with modified method was developed and new hypothesis for the structure
of Membrane Attack Complex (C5b-C9) was constructed during 1974-1984.
Based on the studies of the Complement system a new micro-method for
complement fixation method was elaborated.
Positions
/ special work
and achievements regarding the subject of "Lyme borreliose"
and related:
1980-99: Head of the
Serology
laboratory at Johan Bela Nat. Inst. Hygiene;
during that
periode the laboratory did over 100000 serology tests for Borrelia
burgdorferi, using different methods.
1999: Head
of Lyme
borreliosis center, St Rokus Hosp., Budapest, a
position from
which he had to retire in 1999.
1985: Proposing
the since then worldwide accepted technical term for Lyme Disease
and Related
Disorders that is "Lyme
Borreliosis"at the 2nd World Conference.
????:
Proposing a diagnostic
and therapeutic scheme for Lyme borreliosis seronegatives,
and new hypothesis for
pathogenesis of Lyme borreliosis respectively.
2002-2003/03: Researcher
at
Lyme borreliosis Clinic in Budapest.
2002: Patent 6689577.
Special reagent (Dualdur) and procedure for the detection of pathogens,
especially spirochetes from body fluids by microscopy.
Selected excerpts from the patent description:
"The laboratory diagnosis of borrelioses with different clinical
presentations is based primarily on the detection of spirochetes from
blood samples. This is easily accomplished in recurrent fever because
normally, there is a large number of B.recurrentis present. Besides,
other morphological properties of this pathogen (shown in the table
enclosed) and the fact that this pathogen is easy to stain also make its
detection easier. There are mild cases, however, when the symptoms
suggest the diagnosis of recurrent fever but the cell count is too low
for the conventional methods to detect the causative agent. To solve
this problem, the technique of microhematocrit concentration (double
centrifugation of blood samples) has been used since 1972. Microscopy is
superior in that the test result is not affected by the changing
antigenicity of Borreliae. [Goldsmid, J M. Mohamed: The use of
Microhematrocit Technic for the Recovery of Borrelia duttonii from the
Blood, Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 58:165-169 (1972)].
...
As mentioned above, morphological examination has long been included in
the laboratory diagnosis of spirochetoses. If dark-field microscopy is
employed, concentrated fluid samples do not need to be stained, which
means that the long and thinspirochetes are not washed off the slides,
which, in turn, increases sensitivity.
...
During the first stage of this infection, antibody production is slower
than usual. Antibodies do not appear until weeks after the infection
and are only rarely present throughout the whole course of the disease
because titers keep changing and--after some time--they may become normal
without any intervention. This makes it difficult to define the
threshold titer. There is no clinically applicable threshold that could
make a clear-cut distinction between those who are infected and those
who are not. Besides, generation cycles of the causative agent cause a
fluctuation of the early--IgM type--antibody titers. As far as we know,
this is the only disease in which the causative agent blocks the
production of the more specific and more effective IgG type antibodies,
which normally follows the production of IgM. There are even cases of
Lyme borreliosis in which only the early (IgM type) antibodies are
present years after the infection.
...
What has been said so far affects all antibody assays. That is to say,
comparative studies can only compare the sensitivity of the techniques
in question.
...
Thus, it would be a big mistake to base the laboratory diagnosis of Lyme
borreliosis on the traditional evaluation of a single test. Test
results are sometimes considered non-specific in this case. The chances
of non-specific reactions are known to be higher in spirochetoses but
they can be avoided with traditional pre-test absorption, which removes
the non-specific antibodies that could give a false reaction. If the
test result is negative, physicians may doubt the validity of
the patients' complaints and abandon the possibility of Lyme borreliosis
even though antibody production may be inadequate or blocked, the
technique employed may not be able to detect all antibodies or the
threshold value may not be set correctly.
...
In a study made at a university in Vienna, Austria in 1985, Professor
Stanek and his colleagues found that in artificially infected laboratory
animals bacteremia could be detected using dark-field microscopy as
well as conventional microscopy after Giemsa staining: the Borrelia
burgdorferi sensu lato injected subcutaneously appeared in the
circulation and remained detectable continuously. The number of
bacteria detected was changing in seven to eight day cycles. They
realized that the number of pathogens is changing and that in certain
periods of the generation cycle spirochetes are more difficult to
detect. [(Stanek, G.; Burger, I; Hirschl, A.; Wewalka, G.; Radda, A:
Borrelia transfer by ticks during their life cycle Studies on laboratory
animals. Zbl. Bakt. Mikrobiol. Hyg. A., 263: 29-33: 1986)]
...
In our experience, it is still possible to detect the pathogenic
bacteria if there are less than 10 bacteria in a milliliter of
centrifuged native blood samples. In comparison, the threshold for the
detection of Lyme borreliosis with PCR, which is currently considered
the most sensitive but can only be done in specially equipped
laboratories, is between 40 and 100 germs per ml; besides, as many as
possible primers specific to different sub-strains should be available.
...
It
should be noted that further morphological, immunocytological and
immunoserological examination of the centrifuged sample treated with the
reagent according to the invention is also possible. Furthermore, it
can also be utilized for PCR and cultivation. In the latter cases,
filtering is recommended before concentrating the sample."
2004: The diagnostic method
(DualDur®)
was Patented in USA (Wikipatents, USPTO
). Read more about dr. Bozsik's method below and
here.
????: Founder,
Med, Sec. Head of the Hungarian Lyme Borreliosis Foundation,
Budapest (http://lymenet.hu).
Authorship
of Bozsik BP on subject "Lyme borreliosis":
PubMed search
for "Bozsik+BP"
1985: Borrelia
burgdorferi stained with acidic acridine
orange. Ann. Immunol. Hung. 1985;25:335-344
[Excerpt
on staining of Borrelia spirochaetes:
"Acridine orange,
a fluorochrome dye that at low pH allows differentiation of bacteria,
which show orange fluorescence, from background material and mammalian
cells, which fluoresce green to yellow, is particularly useful for
interpretation of smears prepared from thick or purulent material (58,
99). It also is more sensitive than the Gram stain for detection of
organisms in CSF and other body fluids and in smears prepared from
blood culture broth (103, 104, 126), and in at least one case it
allowed detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in sediment of CSF (20*)" ...
"Wright and Giemsa stains, used routinely in the
hematology laboratory, demonstrate relapsing fever borrelia spirochetes
in stained smears of peripheral blood."
If
published in English? - as title seem to indicate - would it
be possible for you to send me a photocopy, or if published in
Hungarian, make abstract / comment in English?
1987: Bozsik BP, Lakos A, Budai J, Telegdy L, Ambrozy G. Occurrence of
Lyme borreliosis in Hungary. Zentralbl
Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg [A]. 1987 Feb;263(3):466-7. PMID: 3591100
No abstract available.
1990: Kristof
V, Bozsik BP, Szirtes M, Simonyi J. Lyme
borreliosis and Raynaud's syndrome. Lancet.
1990 Apr 21;335(8695):975-6. PMID: 1970048
No abstract available.
1995: Rules of Ticks [Hungarian].
1997: Advice on Tick Diseases [Hungarian].
2000: Bozsik BP. [Management
of Lyme disease][Hungarian]. Orv
Hetil. 2000 Jan 9;141(2):106-11.
PMID: 10686785
No abstract
available.
Would it be possible for you to make abstract / summary in
English?
2002: Bozsik BP. [Comment
on Borrelia burgdorferi Group infections][Hungarian]. Orv
Hetil. 2002 May 26;143(21):1223-4. PMID: 12073543
No abstract
available.
Would it be possible for you to make a abstract / summary in English?
2004: Prevalence of Lyme borreliosis. Lancet. 2004 Mar
13;363(9412):901. PMID: 15031053.
No abstract available, but full text is available
from The Lancet website after login with free registration!
Letter,
excerpt: "Treatment with
antibiotics does
not always result in eradication of
the organism, therefore without follow-up and repeated treatment at
recurrence, Lyme borreliosis chronica can develop. Lyme borreliosis is
often undetectable by serological techniques. In our
practice, the
passive haemag glutination method (Diagast, France) failed to detect
more than 60% of cases, compared with the newer ELISA (Enzygnost,
Behring, Germany). The primary and secondary errors of this passive
haemagglutination method were calculated as 1·9% and 6·3%,
respectively, from 50000 investigations. The significant difference
between these diagnostic techniques highlights the need to assess other
factors, especially clinical symptoms, in the evaluation of results and
formulation of the definitive diagnosis.
The occurrence
of Lyme
borreliosis can be estimated from the reported
incidence of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) and the bacterial (1:10) and
viral (1:1000) infectivity rate of ticks (http://www.tbe-info.com).
The
estimated incidence of TBE in Hungary (population 10 million) is
200–400 cases per year, and the infectivity rate of ticks is 100 times
higher for Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato than for the TBE virus. Thus
there could be more than 20000 new cases of Lyme borreliosis per year
in Hungary. Given
the subclinical nature of the disease, the problems with diagnosis,
misunderstanding about criteria and diagnosis, and the mean age of
patients being 60 years, the number of patients affected at any one
time could be as much as 1million—ie, 10% of the population."
2005 Sheffield, UK, 2005 Lyme
conference presentations.
Read more about
dr. Boszik's practical and theoretical
experience gained from his many years of working with Borrelia
serology and other test methods, as presented by himself in
his PPT-lecture on DIAGNOSIS
(PPT)
and about his experience with successful
treatment of Lyme Borreliosis seronegativa (PPT)
Conclusive
statements by dr. Boszik: Based on 120000 samples
/ 150000 determinations since 1989: Serology test after
chosing the CUT-OFF that gives smallest failures in both
regards for Lyme
borreliosis, will FAIL IN AT
LEAST 7% of all test-results - thereof 5,5% false positives and 1,5%
false
negatives - but in practice serology tests do unfortunately not live up
to the best theoretically possible reliability, rather fails
much more often.
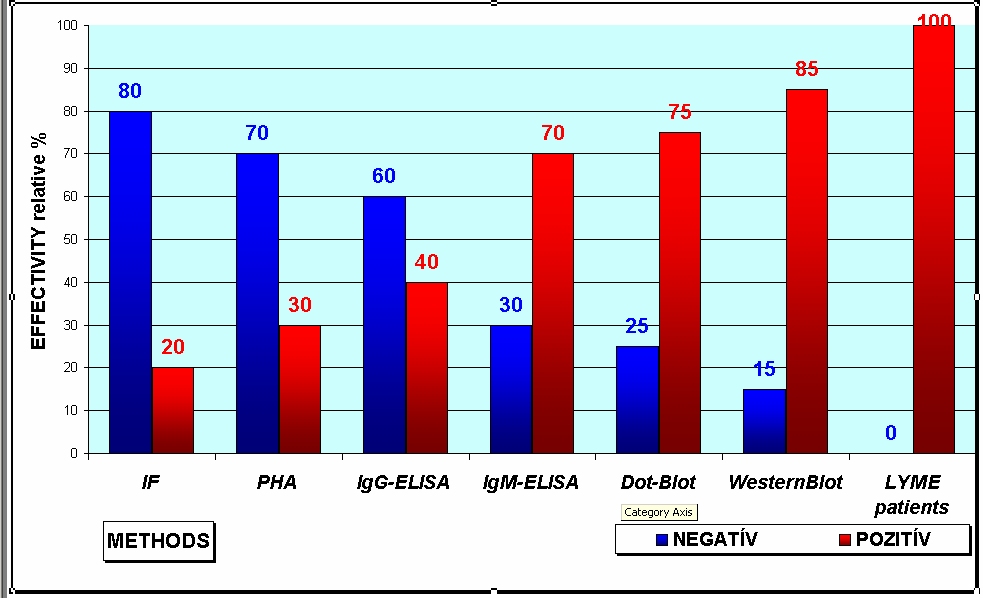
"The
missed proportion of Lyme borreliosis seronegativa was growing with
NEWER methods [PHA 60%, EIA-IgG 30%, EIA-IgM 0% (EIA
Enzygnost)"
"Although 1.5% first order and
5.5% second order error are excellent
results for any laboratory [but
those people misdiagnosed by false positive or negative
serology test
results probably think it is BAD RESULT?] it is astonishing that the
developments
of science give possibility to determine 60% or more cases as people,
who are in bad need of treatment.
This result is neither over-diagnosis,
nor under-estimation especially not false/untrue determinations; they
really belong to both the development of methodology and the epidemic
character of Lyme borreliosis."
IT IS NOT POSSIBLE - and
probably never will become possible
- to safely detect NOR outrule all cases of Lyme borreliosis with one
single serology test method!
"What
is on C6-ELISA? - C6 ELISA
& Wb were identical in 97% at
CDC comparing 180 samples . There was not any reactivity in
Master’s disease, in which B. burgd. sensu lato were isolated
with substrain determination. Masters,E–Philipp,M:
C6 Lyme peptide ELISA serosurvey of Missouri
patients. Abstracts&Presentations at the IX Intl.Conf.
on Lyme borreliosis & Abstract at The Clinical side of
Lyme Disease, N.Y. Augustus 18-22., 2002."
"Closing remarks:
1. Definitive/firm diagnosis for Lyme borreliosis could be set
up with laboratory methods [Dark Field microscopy + other].
2. indication of the treatment is Set up by clinician. Treatment should
be followed/repeated in respect to different sensitivity of different
substrains
3. by control determinations; investigations for 3-5 years."
From the Bozsik "Diagnosis" lecture, Sheffield 2005:
- Spirochetes
could be demonstrated in BLOOD
by dark-field microscopy during
all ACTIVE stages of
pathogenesis!
- 107
of 143 (75%) of the
cases with live
(moving) spirochetes found in their blood by dark-field microscopy,
were confirmed by
real-time PCR
to belong to Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato:
66 (61.7%) B. burgdorferi sensu stricto
20 (18.7%) B. garinii
6 ( 5.6%) B. afzelii and
15 (14.0%) other Borreliae strains than the usual 3 EUROPEAN
strains
Many of these cases were also confirmed by monoclonal
antibody stain for Borrelia burgdorferi with
anti-ospA and
anti-flagellin kindly donated by prof.
Barbour USA. - One
third (1/3)
of these patients with proven LATE Lyme borreliosis were SERONEGATIVE!
Excerpt
from the US
patent description of DualDur®:
"As
the title
suggests, a new reagent has been developed that can slow
down the aging (membrane hardening) of human erythrocytes, leukocytes,
platelets and squamous epithelial cells in the samples. It has been
found that the reagent according to
the invention stops the amoeboid movement of leukocytes and the
fragmentation of platelets. Thus, myeloid figures are not formed. The
membrane of accidentally formed myeloid figures is also hardened.
Consequently, they do not even exhibit Brownian
movement; they simply float along. The movement and the cell division
of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato remained unaffected by the invented
reagent. This is how shedding could be observed, which had only been
noted in cell cultures." .... "The technique according to
the invention makes it possible to study the
current state of pathogenesis and determine the activity of Lyme
borreliosis in a given patient. A fast and reliable diagnosis can be
made even when serological tests are
negative. The reagent and the procedure according to the invention
provides reliable data to aid treatment (which is still controversial),
monitor treatment effects and predict relapses before the development
of humoral immune response or after it has
been blocked and all this is independent of autoimmune responses. "
.... Illustrative picture from abovementioned lecture:
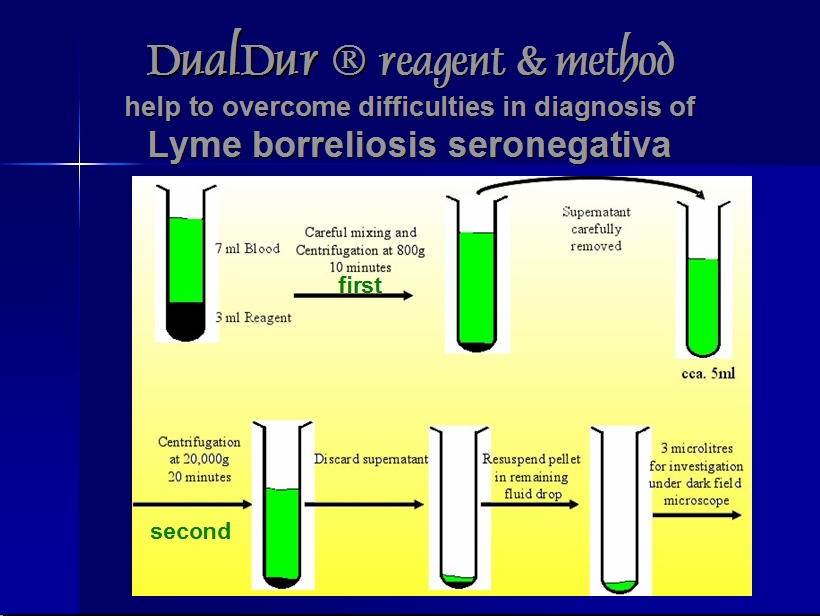
Information about DualDur®
copied from Wilder Network - page three:
"The
results of
the [DualDur®]
test are not influenced by
either the genetic polymorphism or the phenotype of Borrelia
burgdorferi sensu lato (or the changes in either of these during the
pathogenesis of the disease), which is very important in Middle-Europe.
The test is also reliable in the cases when Lyme disease is caused by
new subspecies or immunological changes or when vaccination has
produced an antibody response. The theoretical sensitivity of this
procedure can be as high as one organism/ml. Concurrent PCR tests
appear to be less sensitive even nowadays. If
properly evaluated, it is the most sensitive of the direct tests and it
is also very reliable. It provides a tool to investigate natural
phenomena in a laboratory setting, which may help to gather new
information regarding the pathogenesis of Lyme disease.
In the microscopy, immobile cellular bodies are always seen in the
background serving as controls of the moving Spirochetes.
DualDur®
-treated normal or washed blood or Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato
cultures can also be used as controls. Indirect immunofluorescent
assays using specific monoclonal antibodies kindly donated by
prof. Barbour and Barbara Johnson prove that the Spirochetes are
identical to Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato. They were proven by
electron microscopy in the last years with both negative staining and
immuncytologic reactions.
This
reagent provides
conditions similar to the body, therefore the
division of Spirochetes was detected several times; sometimes they were
acting in pictures. You can see it in the following:

The
next story
will be on the emerging combined
antibiotic treatments
developed in 1990 and used widely with success in Hungary prescribed by
the members of the Therapeutic Workgroup of the Lyme Borreliosis
Foundation in Hungary. According
to our practice we can
tell you that the
following could not
be proved
in Middle Europe: “Conclusion
: Patients with
post-treatment chronic Lyme disease who have symptoms
but show no evidence of persisting Borrelia infection do not show
objective evidence of cognitive impairment. Additional antibiotic
therapy was not more beneficial than administering placebo."
END

Dr. W. Burgdorfer (left), Dr. B.P. Bozsik (in the middle) and
colleague?
From
personal
/ Internet group communications with dr. Bozsik:
Bozsik's own
words on Borrelia burgdorferi Bleb's & Cysts
- see more pictures of Borrelia spirochetes undergoing changes in the PDF:
Please
let me
tell You my opinion based on my morphological practice since 1986.
There
are no
cyst-forms as all ball-like morphology has always some material in them.
They could be differentiate according to the
following :
1. Gemma
has DNA and could be further cultivated. This possibility
was never proved by Garon and Dorward – Personal
communication. If yes, it is the spore, until it is
a sporoid structure.
2. Macromolecular
immunocomplexes (blebs) contain Antigen-Antibody-Complement beside
different
extracellular
material and Osp-s and they never could be used for
cultivations. These forms could be developed during
cultivation as leading character of
B.burgdorferi as other Borrelias do. They are shedding both in the body
and in the cultivation media.
3. So-called Spheroplasts
or L-forms are developing during
the effect of cell-wall-damaging antibiotics, and Lforms are
caused by a process of herniation. They could also have
DNA, but there
is no hypothetical possibility of
cultivation.
4. Further
damaged structures could be detected, which are the final product of protoplasma fragmentation inside
of the Spirochetes – that is the granulation. It is hard to
prove their extracellular presence as the so-called coccoid
forms, except DNA hybridization.
5. Different
forms of the intact B.burgdorferi were demonstrated in cultivation by
Aberer
and Duray and
those of dividing Spirochete by me.
6. Ghost could be appeared as a final state of the
reorganization process of B.burgdorferi after
lytic damage
Do
not forget the Dictionaries:
Gemma \Gem"ma\, n.; pl. Gemm[ae]. [L., a bud.]
1. (Bot.) A leaf bud, as distinguished from a flower bud.
2. (Biol.) A bud spore; one of the small spores or buds in
the reproduction of certain Protozoa, which
separate one at a time from the parent cell.
1.
Gemma -
small asexual reproductive structure in e.g. liverworts and mosses that
detaches from the parent and develops into a
new individual, reproductive structure - the parts of a plant involved
in its reproduction)
Detailed you can find in
my
lectures hold at the Anniversary
Congress of Lyme Borreliosis Foundation in Budapest in
2000 about the DualDur® reagent and method and the Hypothesis
based on the results got with this
method. The complete summary could be
downloaded at www.lymenet.hu
(letoltheto anyagok) and further information
from now http://lymerick.net/videomicroscopy.htm
All of my investigation
was made
in native human blood samples with Dark-field microscopy.
More from the conference website: Information
to patients about
Lyme borreliosis (10 pages, English version), Questionnaire (1
page, English version, Word DOC),
Bozsik (2000) PPT on Therapy
and Bozsik (2000) PPT on Diagnosis.
PS: I have never
prescribed as I am a retired pathologist, but proposed to use and our
colleagues are using tinidazol with our combined treatment schedule
with better effect than without it to be demolish Gemma-s.
I wish to know your proposal for patients with sensitivity to “azols”.
Alinia? Plaquenil? Have you practice with it? Crossreaction
with other antibiotics? Thanks You in advance, Bela
Mail to MMI-list 11. Sept. 2007:
Dear Colleagues and Members of the list!
Binding antibody to the
protein-band of 41 means
appearance of LB either in the past or in the days. Other positive binding help
us to evaluate a firm positive reaction. Perhaps the formerly
reagents could not avoid the cross-reaction, so there were period of time with
the need of clinical differentiations. Sometimes a one-shot abx
treatment causes decapitation of the immune-response and develops LB
seronegativa with a weak or no reaction even to p41. Seropositivity otherwise
means only that LB exists.
The indication of the
treatment belongs to the clinical symptoms at this moment. – The only
absolute indication of the treatment is the PCR positivity of the biting tick.
[??? why do you NOT mention PCR positive on PATIENT SAMPLE?].
The substrain(s) determination gives a good data for the personal antibiotic
treatment-schedule in the Carpathian Basin and Europe, too. There are further
subgroups of Borrelia
burgdorferi sensu stricto with
different pathogenicity, which could also differ in their sensitivity to
antibiotics.
Think of the extreme
genetic plasticity and adoptability of Borrelia
burgdorferi sensu lato we should prescribe
combined antibiotics not allow the adoptation of the causative
agent.
There is a possibility to
investigate Bbsl in blood using DualDur® reagent and method to help
with further data the clinicians. This reagent and method was developed in 1986.
You can see the demo video at the lower end of the page for http://lymerick.net/videomicroscopy.htm
with some words on my video: http://lymerick.net/Sheffield2005/Bozsik/Dualdur.wmv
This method
gives a possibility for further analysis of Borrelia
burgdorferi sensu lato in similar condition to the
body. Summarizing: there are
two main and different chapters in
Lyme borreliosis.
1.
Diagnosis
of LB according
to laboratory investigations
2.
Indication
of treatment according
to the activity of clinical symptoms
Of course there are several
not classified parts both of diagnosis and indication of treatment, especially
in the process of the development of a personal schedule for
treatment.
3.
The
differential diagnosis of other TBD
should be introduced into these processes…
Best
wishes
Bela
This article
was proof read by and further comments made by Dr. Bozsik (October
2007), but some of the excerpts has been added since.